Deschutes County Health Data
Find data on a variety of health topics for our community here.
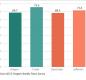
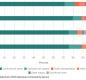
Demographic factors like population density, education level, household income, age distribution of the population, and poverty, among others, influence the health of our community.
In 2017, we updated the 2015 Central Oregon Regional Health Assessment (RHA) with new data. This page provides an overview of updated data on demographics. Please read through the information below, or download the demographics overview handout from the supporting documents section at the bottom of the page.
Chronic diseases are conditions that a person may live with for many years or a lifetime. Chronic diseases can lead to early death, decreased quality of life, and increased personal healthcare spending.
In 2017, we updated the 2015 Central Oregon Regional Health Assessment (RHA) with new data. This page provides an overview of updated data on chronic diseases. Please read through the information below, or download the chronic diseases overview handout from the supporting documents section at the bottom of the page.
The health of a child begins with a healthy mother and a healthy pregnancy. Factors like not using tobacco, alcohol, or other drugs, maintaining a healthy weight, receiving prenatal care, maintaining good oral health, breastfeeding, and preventing injuries and adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) are key for starting an infant's life in a healthy manner.
Children are exposed to and react to environmental and physical exposures differently than adults. Adolescents are entering a time in their lives when they are establishing health patterns and behaviors. Ensuring their safety and knowledge of health behaviors is vital to their overall health.
Mental health is important at every stage of life, from childhood and adolescence through adulthood. While good mental health is associated with positive health outcomes, mental illnesses are associated with poor health outcomes like chronic diseases and injuries.
Substance use is associated with higher rates of all-cause mortality and chronic disease. Heavy substance use is also a risk factor for motor vehicle fatalities, fetal alcohol syndrome, interpersonal violence, overdose, and STIs. Research suggests that the earlier in life a person begins to use substances, the more likely he or she is to develop serious problems with addiction.
Some injuries are considered unintentional, meaning there was no intent to do harm. Unintentional injuries are preventable events and are no longer considered "accidents." Many behaviors have been put in place over the last several decades to reduce unintentional injuries, including seatbelt use in cars, increased helmet use while riding bikes, and using life jackets in the water, among many others.
Dental cavities are largely preventable. However, tooth decay is one of the most common chronic diseases among children. Untreated tooth decay can cause problems with eating and speaking and can cause pain, which can disrupt learning and personal growth.
Ensuring access to healthcare is important. A variety of factors can lead to varying access to healthcare, like socioeconomic status, language or cultural barriers, or environmental factors like availability of services and transportation.
Where people work, live, and play can dramatically affect their health. Environmental health "addresses the physical, chemical, and biological factors external to a person, and all the related factors impacting behaviors" (World Health Organization). These topics include things like air quality, water quality, the built environment, and consumer product exposures.
Health-related quality of life includes the physical, mental, and emotional well-being of an individual. Health-related quality of life is associated with chronic disease prevalence and risk factors. Length of life is influenced by a variety of factors, including disease, health events, and social determinants of health. The public health and healthcare systems work to address health inequities that lead to reduced quality and length of life.